Control Charts Are Used to Check Which of the Following
Control charts ushered in by Walter Shewhart in 1928 continue to provide real-time benefits in todays modern factories. This chart is a graph which is used to study process changes over time.
Which of the following criteria is not used to determine if a control chart indicates a process that is statistically out-of-control.
. The descriptions below provide an overview of the different types of control charts to help. One method of tracking involves the use of process control charts. It is more appropriate to say that the control charts are the graphical device for Statistical Process Monitoring.
The following table may be utilized to help select an appropriate control chart for each application. To determine the average amount. The control limits on both chats are used to monitor the mean and variation of the process going forward.
We measure weight height position thickness etc. To determine if the process is in control only common cause variation see Jan 2004 e-zine on the website To show the result of improvement efforts. There are 8 consecutive points all above or all below the centerline.
Keep those Six Sigma DMAIC Improvements. It helps us to keep an eye on the pattern over a period of time - variation quantity the current capability of your process and identify when some special events interrupt the normal operations. Standard Deviation S control chart.
Control charts are a great tool that you can use to determine if your process is under statistical control the level of variation inherent in the process and point you in the direction of the nature of the. The control limits on both chats are used to monitor the mean and variation of the process going forward. If we cannot represent a particular quality characteristic numerically or if it is impractical to do so we then often resort to using a quality characteristic to sort or classify an item that is inspected into one of two.
As with the other control charts special cause tests check for outliers and process shifts. Select the best definition of a control chart. It provides a picture of the process variable over time and tells you the type of variation you are dealing with as you move forward with continuous improvement.
Managers must make a number of important decisions about the use of. The ranges are now recorded onto a control chart. Control Charts for Variables 2.
When they were first introduced there were seven basic types of control charts divided into two categories. Variable Data Charts IX-MR individual X and moving range Xbar-R averages and ranges Xbar-s averages and. This is the range R of the set of data.
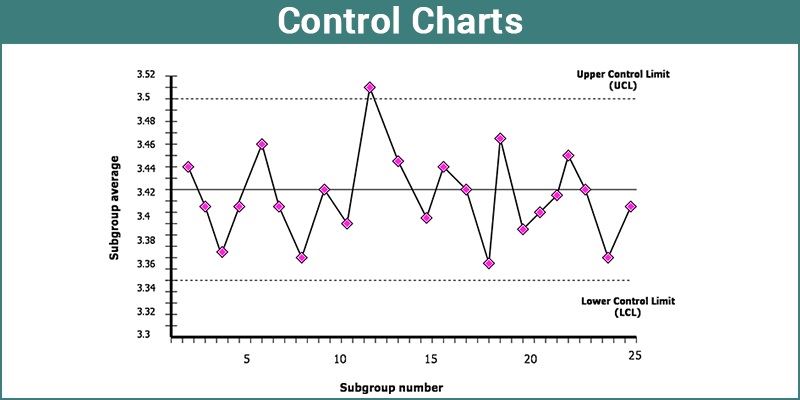
A p-charts B R-charts OC X-bar charts OD C-charts Used to monitor the number of defective items in a process. In statistics Control charts are the tools in control processes to determine whether a manufacturing process or a business process is in a controlled statistical state. A control chart always has a central line for the average an upper line for the upper control limit and a lower line for the lower control limit.
Control charts also known as Shewhart charts or process-behavior charts are a statistical process control tool used to determine if a manufacturing or business process is in a state of control. If a point is out of the control limits it indicates that the mean or variation of the process is out-of-control. The S chart can be applied when monitoring variable data.
For each set of date the difference between the smallest and largest readings are recorded. Control Charts Project Tools Six Sigma. The charts are segregated by data type.
This article throws light upon the two main types of control charts. So A process is considered in-control if all the data points collected fall within the Control Limits of a Control Chart more on trending below. These charts are used to achieve and maintain an acceptable quality level for a process whose output product can be subjected to.
There is a pattern trend or cycle that is obviously not random. Data are plotted in time order. The proportion of defective items generated by a process.
In the Improve phase Control Charts are used to see the process improvement. For instance if you review all loan applications each week and the number submitted differs on a weekly basis you could. Control Charts for Attributes.
The control chart is a graph used to study how a process changes over time. A time-ordered plot of sample statistics used to determine randomness or non-randomness. Control charts have two general uses in an improvement project.
The x-bar and R-chart are quality control charts used to monitor the mean and variation of a process based on samples taken in a given time. Used to monitor the dispersion of a process. Control charts are a great tool to monitor your processes overtime.
Traditional control charts are mostly designed to monitor process. Control charts are simple but very powerful tools that can help you determine whether a process is in control meaning it has only random normal variation or out of control meaning it shows unusual variation probably due to a special cause. To determine the spread about the average.
These charts are also known as Shewhart charts or process-behavior charts. A control chart is used to monitor a process variable over time. A less common although some might argue more powerful use of control charts is as an analysis tool.
The Shewhart control chart plots quality characteristics that can be measured and expressed numerically. The main purpose of control charts is to help determine if a process is stable and in-control or unstable and out-of-control. Steven Wachs Principal Statistician Integral Concepts Inc.
If a point is out of the control limits it indicates that the mean or variation of the process is out-of-control. Control Charts for Variables. Every Control Chart has an Upper Control Limit UCL and a Lower Control Limit UCL.
There is a point lying beyond the upper or lower control limits. The x-bar and s-chart are quality control charts used to monitor the mean and variation of a process based on samples taken in a given time. Check all that apply OA p-chart B R-chart C X-bar chart D C-chart Which of the.
The most common application is as a tool to monitor process stability and control. When a process is stable or in control this means that it is predictable and affected only by normal random causes of variation. A C-charts B p-charts C X-bar charts D R-charts Which of the following control charts use attributes.
In an earlier post I wrote about the common elements that all control charts share. The purpose of a control chart is to set upper and lower bounds of acceptable performance given normal variation. That variable can be in any type of company or organization - service manufacturing non-profit and yes healthcare.
I can use a control chart to do the following. Shewhart chart statistical process control chart. Control charts are a key part of the management reporting process that have long been used in manufacturing stock trading algorithms and process improvement methodologies like Six Sigma and Total Quality Management TQM.
This way you can easily see variation. These limits are used to determine if a process is in-control or out-of control. Once you have established an objective the next step is to select the type of control chart to use.
Charts for variable data are listed first followed by charts for attribute data. The center line is the averages of all the ranges. Control Charts are used to focus on detecting and monitoring the process variation over time.
U charts The u chart is a more general version of the c chart for use when the data points do not come from equal-sized samples.
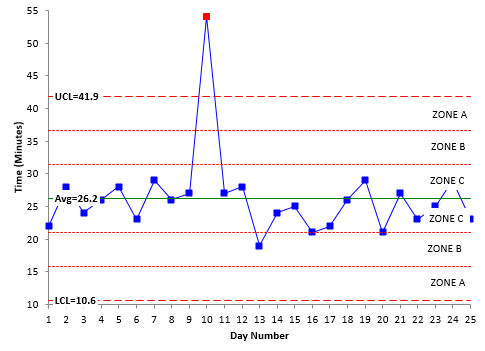
Control Chart Rules And Interpretation Bpi Consulting
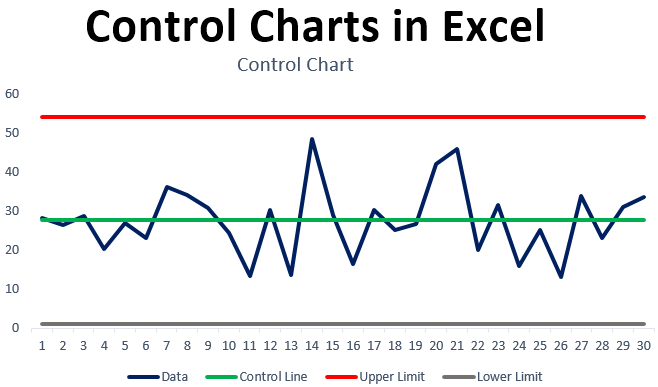
Control Charts In Excel How To Create Control Charts In Excel
No comments for "Control Charts Are Used to Check Which of the Following"
Post a Comment